Uncategorized
How Bitdeer Is Transforming Bitcoin Mining Machines

Application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) chips form the backbone of the bitcoin (BTC) mining industry. ASIC machines are made for a single purpose: To solve Bitcoin’s SHA-256 algorithm as fast as possible in order to collect block rewards.
They’re extremely good at it. One of the most widely used ASIC machines, the Antminer S19, is capable of making 82 trillion computations per second — 820 times the number of stars in the Milky Way. The $30 billion ASIC manufacturing market is dominated by Bitmain. The Chinese company’s machines power roughly 80% of Bitcoin’s hashrate, according to TheMinerMag.
But Singapore-based bitcoin mining firm Bitdeer (BTDR) intends to shake things up with the release of a new ASIC chip architecture. These new chips could bring a huge jump in efficiency, the company claims, while improving transparency in the ASIC manufacturing process.
“The two dominant players [Bitmain and MicroBT] are both private companies, and very opaque,” Jeff LaBerge, head of capital markets and strategic initiatives at Bitdeer, told CoinDesk in an interview. “They don’t really engage with the media or give any type of guidance about what they’re doing from an R&D standpoint, and that makes it very difficult for end-buyers to plan.”
“We want our customers to know where we’re at in our manufacturing process, what our roadmap is in terms of new chip designs, where we’re at in our production cycles,” LaBerge said.
Shanon Squires, chief mining officer at bitcoin hosting firm Compass Mining, told CoinDesk that increased visibility into ASIC production would help miners plan new hardware shipments and make it easier to predict Bitcoin’s difficulty growth. “Bitdeer’s commitment to transparency is great for the mining industry,” she said.
“While Canaan discloses its annual sales volume for various mining models, Bitdeer takes it a step further by providing more frequent delivery volume updates,” Wolfie Zhao, head of research at TheMinerMag, told CoinDesk. “Although both are smaller players in the hardware market, their efforts show good faith in promoting transparency. Hopefully, this will encourage the larger market incumbents to take note.”
Seeking efficiency
ASIC chips have used mostly the same blueprint since 2014. Over the last decade, the biggest increases in ASIC power efficiency have come at the foundry level, as leading global chipmaker TSMC has refined its manufacturing process. While miners have also made alterations to chip design, such modifications have only brought incremental gains.
Even so, progress has been tremendous. The very first ever ASIC, Canaan’s Avalon (2013) had a power efficiency of 6,000 joules per terahash (J/TH). Bitmain’s Antminer S21XP Hydro, the current most efficient machine on the market, boasts 12 J/TH efficiency.
Bitdeer, which is listed on Nasdaq, wants to create a completely new architecture for its ASICs. “We feel like it’s going to be necessary to break into what we call the single-digit efficiency range,” LaBerge said, referring to mining rigs with less than 10 J/TH in efficiency.
Scaling up with the traditional blueprint means using progressively thinner chips. But thinner means chips are more likely to be defective and yields per batch tend to fall. “You’re also competing with Apple and Nvidia and some of the biggest companies in the world for the same materials,” LaBerge said.
Bitdeer’s Chief Strategy Officer, Haris Basit, is leading a team of engineers to create a new framework. Some members of that team worked on designs found in Bitmain’s first ASIC chips back in 2014 — the chips whose architecture became the standard across the industry. (Bitmain did not respond to a request for comment.)
Bitdeer’s research has already had successes. The company’s most recent product, the SEALMINER A3, achieved a power efficiency of 9.7 J/TH during performance trials, the firm reported on Monday. That means the A3 — which still uses the traditional ASIC blueprint — could end up taking the efficiency crown from the S21XP Hydro.
Yet the miner’s SEALMINER A4, which will employ the firm’s new chip architecture, is expected to consume 5 J/TH. It will likely be the most efficient ASIC machine on the market by a significant margin.

“People have known for a long time that you could recycle [the electric] charge on a chip, but no one’s really been able to figure out how to do that in a way that allows for high performance… We’ve cracked the code on how to do this in a very high performance application,” Basit told the Coin Stories podcast in December.
“Instead of just using [charge] once and discharging it, we use it several times, four, five, six times. So we get [a] 75-80% improvement in efficiency by doing that,” Basit added.
“Our SEALMINER A4 chips will use this technology, but it should also be applicable more generally in digital chips, especially digital chips that are highly active, like GPUs and signal processing chips.”
Manufacturing chips
Making ASICs isn’t easy. Bitdeer’s research team is divided into two units (one in Singapore, another in Silicon Valley) that both work on new chip designs. “For such a simple machine — all it does is solve the SHA-256 algorithm — it’s extremely complicated to design. We’ve got some of the best engineers in the world working on this,” LaBerge said. The company spends approximately $6-8 million on research per quarter.
So far, the firm has been delivering new products at a fast pace. Bitdeer pushed out both the SEALMINER A1 and A2 in 2024 and is expecting the A3 to enter mass production in the latter half of 2025. It says the A4 should reach tape-out (the last stage of its designing process) in the third quarter of the year, with a release likely in late-2025 or early 2026.
When a new chip design is finalized, Bitdeer sends the plans over to TSMC. Not only is the Taiwanese firm the largest chip manufacturer in the world, it’s also the most advanced on a technological level, which makes Bitdeer’s partnership with it crucial.
“You can’t just go to TSMC and say, ‘Hey, I want 100 exahash worth of chips in the next three months.’ There’s a process for going through that,” LaBerge said. “You go in and ask them for chip allocation, and they’ll give that based on priority.”
Once it has the plans in hand, TSMC produces a mask, which essentially functions as a template for chips — like the platen in a printing press. The mask is sent to Bitdeer alongside risk chips (a small batch of chips that the company can use for trials) to make sure the design works properly. If the firm needs any alterations to be made to the design, that’s when it happens. In that case, TSMC makes corrections based on Bitdeer’s feedback and sends over a new mask with new risk chips. All of this happens at significant cost. Bitdeer spent $14 million on the A2’s tape-out and $26 million on the A3’s.
When Bitdeer is satisfied with a design, TSMC uses the mask to mass-produce wafers. LaBerge compared wafers to sheets, each containing hundreds of chips. Technically, a mask can be used to create an almost unlimited number of wafers, but TSMC has finite resources and can only produce a certain number of chips, so firms end up competing for them.
One of the advantages of the A4’s design, according to LaBerge, is that it’s supposed to make the firm’s chip allocation process easier. “[Basit] challenged the team to come up with a new architecture that didn’t need to undergo TSMC’s latest processes, but could step back a couple of generations, which would allow us to use a node that is much less in demand,” he said. A semiconductor node is basically a specific version of the firm’s chip manufacturing technology; TSMC is constantly building new nodes in an effort to refine its processes.
It takes roughly three months for Bitdeer to receive its mask and risk chips after first submitting its design to TSMC. Then, it’s another three or four months for the company to receive its chips once it has given the foundry the green light for mass production. The chips are sent straight to Bitdeer’s manufacturing facilities in Asia. From there, it can take four to eight weeks for the mining rigs to be fully built and packaged.
Aiming for the top
Despite all the costs incurred during production, some of the capital required for manufacturing ASICs comes from Bitdeer’s customers.
Miners interested in purchasing Bitdeer’s ASICs typically put down a deposit of 25% to 50% of the total cost of the order. The production cycle tends to average at six to seven months, so it doesn’t take long for the company to recuperate its funds and make a profit.
Building ASICs also creates advantages for Bitdeer’s own mining operations. Up until recently the firm, which was founded in 2021, focused on the hosting business, meaning that it provided facilities for other bitcoin miners to place their rigs. Bitdeer is slowly transitioning out of that model and expanding its own mining operations alongside its ASIC manufacturing arm.
The acquisition of ASICs is typically the most expensive part of building up a bitcoin mining operation. These machines usually only last around three or four years before newer models make them obsolete, so bitcoin mining firms are constantly looking to acquire more.
Not only is Bitdeer able to considerably reduce these costs by producing its own machines, but it also has the option of selling its mining rigs to other firms depending on its needs.
Down the line, Bitdeer aims to give Bitmain and MicroBT a run for their money, and disrupt what LaBerge called the duopoly of the ASIC market. “We want to be the top player in the market, absolutely,” LaBerge said. “We believe we have the team and the technology to do that.”
UPDATE (March 14, 2025, 15:30 UTC): Added the cost of the SEALMINER A3 tape-out.
Uncategorized
Trump’s Official Memecoin Surges Despite Massive $320 Million Unlock in Thin Holiday Trading

TRUMP, the memecoin tied to U.S. President Donald Trump, gained more than 9% in the past 24 hours following a $320 million token unlock. The price now sits around $8.40, still down more than 88% from its peak above $71 on Jan. 18.
The recent unlock may spell further trouble for investors, who are estimated to have lost a total of $2 billion after purchasing the token earlier this year.
Token unlocks typically flood the market with new supply and tend to depress prices. But in this case, the market appears to have priced in the release beforehand, potentially explaining the price uptick. Still, the $320 million unlock raises the risk of a large sell-off, especially given TRUMP’s thin liquidity.
Data from CoinMarketCap shows that just $1.3 million could move the token’s price by 2% on major exchanges. The move also comes during the Easter holiday weekend, when trading volumes are subdued and price swings can be more pronounced.
On social media, rumors are swirling about a possible event for large token holders, supposedly being organized by Trump himself. These claims remain unverified and highly speculative.
Data from Dune analytics shows there are currently 636,000 TRUMP token holders on-chain, with just 12,285 wallets having more than $1,000 worth of the cryptocurrency.
Uncategorized
Slovenia Moves to Tax Crypto Profits at 25%

Slovenia’s finance ministry has proposed a 25% tax on capital gains from cryptocurrency starting in 2026, under a draft law aimed at closing a gap in the country’s tax system.
The tax will apply to profit made when individuals sell crypto for fiat currency or spend it on goods and services. However, swapping one cryptocurrency for another will remain tax-free, and any gains made before January 1, 2026, will not be taxed, according to the finance ministry’s proposal.
The measure is meant to treat crypto gains more like other capital investments, such as stocks or bonds, which are already taxed.
Under the law, individuals would calculate their profit as the difference between the value at acquisition and at sale, adjusted for transaction fees. Losses can be carried forward to offset future gains. Taxpayers would need to file an annual return by March 31 and make payment within 15 days.
The tax could generate between €2.5 million and €25 million annually, according to preliminary government estimates. The country’s Ministry of Finance is soliciting public feedback on the proposal, which would come into effect next year.
The proposal comes as data from the European Central Bank’s ‘Survey on Consumer Payment Attitudes in the Euro Area’ shows Slovenia has the highest share of cryptocurrency owners in the euro area, with 15% of adults holding digital currencies last year, up from 8% in 2022.
Disclaimer: Information collected for this article was translated with the use of artificial intelligence.
Uncategorized
Unpacking the DOJ’s Crypto Enforcement Memo

Earlier this month, the Department of Justice disbanded its National Cryptocurrency Enforcement Team and said it would no longer pursue what Deputy Attorney General Todd Blanche described as «regulation by prosecution.»
You’re reading State of Crypto, a CoinDesk newsletter looking at the intersection of cryptocurrency and government. Click here to sign up for future editions.
‘Regulation by prosecution’
The narrative
The U.S. Department of Justice «will no longer pursue litigation or enforcement actions that have the effect of superimposing regulatory frameworks on digital assets» in lieu of regulatory agencies putting together their own frameworks for overseeing the sector, a 4-page memo signed by Deputy Attorney General Todd Blanche on April 7 said. In other words, the DOJ will no longer pursue «regulation by prosecution,» the memo said.
Why it matters
The DOJ’s memo raised concerns that it may mean criminal activities in the crypto sector would not be prosecuted, or at least prosecuted as heavily as it was under the past several years — both by disbanding the National Cryptocurrency Enforcement Team (NCET) and by shifting the entity’s priorities.
Breaking it down
At a practical level, the memo itself is internal guidance but may not be a binding document. Multiple attorneys told CoinDesk they interpreted the guidance to indicate that the DOJ would still bring fraud or other criminal cases involving crypto, but would try to avoid any cases where the DOJ itself had to determine if a digital asset was a security or a commodity.
«Fraud is still fraud,» said Josh Naftalis, a partner at Pallas Partners LLP and a former prosecutor with the U.S. Attorney’s office for the Southern District of New York. «This memo does not seem to say the DOJ is not going to prosecute fraud in the crypto space.»
Still, the memo raised alarms for prominent Democrats who questioned whether the DOJ was suggesting it would let criminal conduct occur. Senators Elizabeth Warren, Mazie Hirono, Richard Durbin, Sheldon Whitehouse, Christopher Coons and Richard Blumenthal wrote a letter to Blanche, saying his «decision to give a free pass to cryptocurrency money launderers» and shut down the NCET were «grave mistakes that will support sanctions evasion, drug trafficking, scams and child sexual exploitation.»
«Specifically, the Department will no longer target virtual currency exchanges, mixing and tumbling services and offline wallets for the acts of their end users or unwitting violations of regulations — except to the extent the investigation is consistent with the priorities articulated in the following paragraphs,» the DOJ memo said, a passage the Senators’ letter referenced.
New York Attorney General Letitia James wrote an open letter to Senate leaders in the same week asking them to advance legislation to address cryptocurrency risks. She did not specifically reference Blanche’s memo but detailed possible ways to better police the sector through legislation.
Katherine Reilly, a partner at Pryor Cashman and a former prosecutor with the U.S. Attorney’s Office for the Southern District of New York, told CoinDesk that most of the major crypto cases brought by the DOJ in recent years would not have been affected had this guidance been in effect.
The BitMEX case in 2020, when the DOJ and Commodity Futures Trading Commission brought unregistered trading and other charges against the platform, is «probably closest to the line» of being a case that may not have been brought under this guidance, she said.
Trump pardoned BitMEX, its founders and a senior employee in late March, barely two weeks before the DOJ memo was shared.
«I think that it’s clear that the Justice Department wants to limit the DOJ’s role in regulating the crypto industry … looking beyond its role in other crimes, fraud, laundering proceeds from narcotics trafficking, things like that, and sort of take a step back from the role of trying to bring order and fairness to the crypto industry as a whole,» Reilly said.
That’s «probably the intent behind the BitMEX pardons too,» she said.
Naftalis said the DOJ will continue to pursue drug, terrorism or other illicit financing charges even under the memo.
«I think that the headline for the industry is to the extent that there are legal uses of crypto, they’re not going to set the guard rail by criminal enforcement,» he said. «That’s for Congress.»
One section of the memo tells prosecutors not to charge Bank Secrecy Act violations, unregistered securities offering violations, unregistered broker-dealer violations or other Commodity Exchange Act registration violations «unless there is evidence that the defendant knew of the licensing or registration requirement at issue and violated such a requirement willfully.»
Carla Reyes, an Associate Professor of Law at SMU Dedman School of Law, told CoinDesk that this may be referencing recent cases where developers build tools under the impression that they were not committing unlicensed money transmitting activities under existing guidance but may get charged anyway.
«Most criminal statutes require some level of knowledge to define your intention, and knowledge that you’re committing a crime when you do it,» she said. «The further away you get from that, the lesser the charge, but the more willful [and] intentional it is, the higher the charge.»
What the memo seems to want to explicitly move away from is any suggestion that federal prosecutors would interpret how securities or commodities laws might apply to digital assets.
«Prosecutors should not charge violations of the Securities Act of 1933, the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Commodity Exchange Act, or the regulations promulgated pursuant to these Acts, in cases where (a) the charge would require the Justice Department to litigate whether a digital asset is a ‘security’ or ‘commodity,’ and (b) there is an adequate alternative criminal charge available, such as mail or wire fraud,» the memo said.
A popular critique leveled against former SEC Chair Gary Gensler by the crypto industry was that he was «regulating by enforcement,» rather than focusing on developing guidance for the industry to know what was or wasn’t acceptable. Blanche seems to be referring to a similar critique in the memo, Naftalis said, in that one-off enforcement decisions by the SEC or DOJ should not define the guardrails for the industry.
Steve Segal, a shareholder at Buchalter, said that some of the DOJ’s past cases would charge trading venues for failing to police their own customers. The memo now seems to suggest that if a crypto exchange’s executives were running a clean platform, and customers were laundering funds derived from criminal activities, the executives would not be charged. This is in contrast with, for example, FTX, where the executives were charged and convicted of (or pled guilty to) fraud charges.
«Of course, a lot of the big crypto cases we’ve seen over the last few years are sort of pure investor fraud, things like FTX. And one of the more interesting things about this memo is it talks about crypto investors and really prioritizing cases where crypto investors are being victimized,» Reilly said. «And so I don’t think we should conclude that this memo means we’re going to see a lot fewer cases in the crypto space, or that crypto companies can sort of breathe a sigh of relief that the DOJ is out of the picture for a few years.»
The DOJ’s future cases may appear a bit different in terms of the specific allegations made, but «it’s much too soon to say that everybody can assume the DOJ is out of the crypto business,» she said.
Many of the attorneys speaking to CoinDesk agreed that the memo itself did not clarify all of the different issues that may come up with a criminal case, nor was it an end-all/be-all document.
The memo announced prosecutorial discretion but it isn’t itself a law, Reyes said, adding that it may guide internal decision-making about which cases to pursue the most heavily, as well as the strategies that guide those prosecutions.
A lot of details about how this memo ties together with Trump’s executive order on the strategic bitcoin reserve still need to be spelled out, Segal said. Sections on victim compensation and how seized funds should be handled in the memo do not explain how the DOJ might handle situations where seized funds are turned over to bankruptcy estates, such as what happened with FTX or other similar scenarios.
«I think we’ll really have to see how it plays out, because this guidance, I do think, leaves prosecutors a lot of room to bring cases even of these kinds of violations that are being cast as more regulatory,» Reilly said. «So even if that’s the intent, I think the devil is in the details on what cases we see going forward.»
Stories you may have missed
- U.S. Crypto Lobbyists Flooding the Zone, But Are There Too Many?: Jesse Hamilton took a look at the number of Washington, D.C.-based crypto lobbyist groups now active.
- Feds Mistakenly Order Estonian HashFlare Fraudsters to Self-Deport Ahead of Sentencing: Ivan Turogin and Sergei Potapenko, who were extradited from Estonia to the U.S. on charges tied to the HashFlare Ponzi scheme, await sentencing after pleading guilty to one conspiracy charge each earlier this year. Though they’re under a court order to not travel before their sentencing, they received an email from the Department of Homeland Security telling them to self-deport, seemingly by mistake.
- Kraken Sheds ‘Hundreds’ of Jobs to Streamline Business Ahead of IPO, Sources Say: Kraken cut 400 roles last October, which at the time was about 15% of its workforce. It’s since continued shedding jobs, Ian Allison reports.
- Republican States Pause Lawsuit Against SEC Over Crypto Authority: A group of Republican Attorneys General have filed to pause a lawsuit against the Securities and Exchange Commission alleging its crypto enforcement actions intruded into state regulators’ remits.
- Crypto Casino Founder Richard Kim Arrested After Gambling Away Investor Funds: Zero Edge founder Richard Kim was arrested this week on wire and securities fraud charges after allegedly losing «nearly all» of the $7 million he raised from his investors. Kim told CoinDesk last year that he had gambled over $3.6 million of his investors’ funds away.
This week
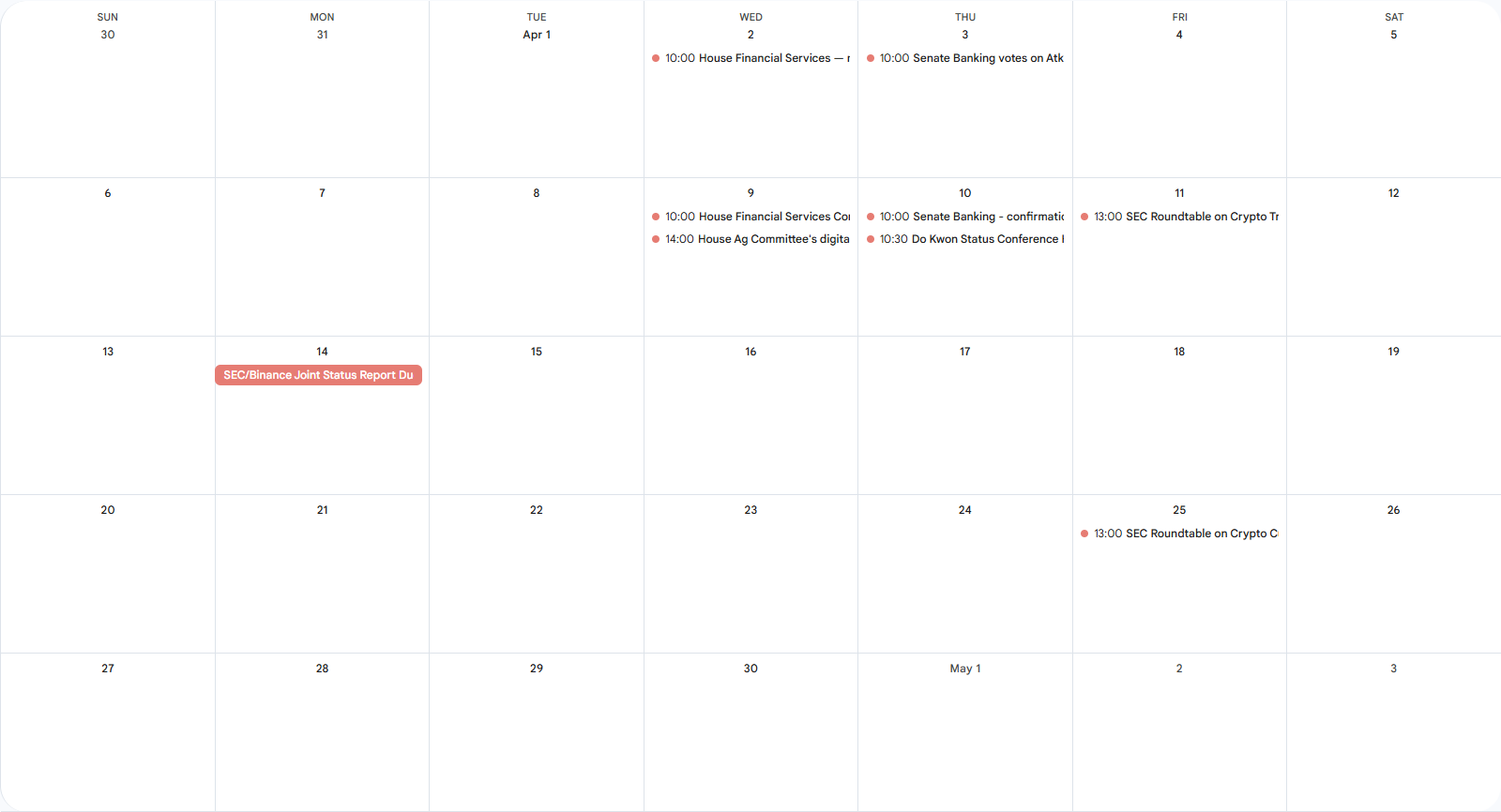
Monday
- The Securities and Exchange Commission and Binance were set to file a joint status report on their discussions after a judge paused the regulator’s case against the exchange and its affiliated entities and executives in February. Last Friday, the parties asked for an extension of this deadline, and the judge overseeing the case signed off on Monday, giving the parties until mid-June to file a follow-up.
Elsewhere:
- (The Wall Street Journal) Binance executives met with U.S. Treasury Department officials in March about potentially «loosening U.S. government oversight» of the exchange following Binance’s November 2023 guilty plea, the Journal reported. Binance agreed to a court-appointed monitor as part of the plea. At the same time as last month’s discussions, Binance was in talks with the Trump-backed World Liberty Financial to develop a dollar-pegged stablecoin.
- (Fortune) Fortune spoke to and profiled Bo Hines, the executive director of U.S. President Donald Trump’s digital assets advisory council.
- (CNBC) U.S. importers are seeing more «canceled sailings» due to a drop in demand as a result of tariffs, CNBC reports.
- (The Verge) ICERAID claims to be a protocol on Solana where people can crowdsource images of «criminal illegal alien activity» in exchange for tokens, but it does not appear to have any connection to Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), The Verge reports.
- (NPR) The Department of Homeland Security is revoking parole for a number of migrants, telling them to self-deport from the U.S. U.S. citizens, born within the U.S., are also receiving these emails.
- (The New York Times) Acting IRS Commissioner Gary Shapley has been replaced after just three days on the job, after Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent reportedly complained to President Donald Trump that he was not consulted on Shapley’s promotion, which was pushed by Elon Musk.
If you’ve got thoughts or questions on what I should discuss next week or any other feedback you’d like to share, feel free to email me at nik@coindesk.com or find me on Bluesky @nikhileshde.bsky.social.
You can also join the group conversation on Telegram.
See ya’ll next week!
-

 Fashion6 месяцев ago
Fashion6 месяцев agoThese \’90s fashion trends are making a comeback in 2017
-

 Entertainment6 месяцев ago
Entertainment6 месяцев agoThe final 6 \’Game of Thrones\’ episodes might feel like a full season
-

 Fashion6 месяцев ago
Fashion6 месяцев agoAccording to Dior Couture, this taboo fashion accessory is back
-

 Entertainment6 месяцев ago
Entertainment6 месяцев agoThe old and New Edition cast comes together to perform
-

 Sports6 месяцев ago
Sports6 месяцев agoPhillies\’ Aaron Altherr makes mind-boggling barehanded play
-

 Business6 месяцев ago
Business6 месяцев agoUber and Lyft are finally available in all of New York State
-

 Entertainment6 месяцев ago
Entertainment6 месяцев agoDisney\’s live-action Aladdin finally finds its stars
-

 Sports6 месяцев ago
Sports6 месяцев agoSteph Curry finally got the contract he deserves from the Warriors





