Uncategorized
Bitcoin’s Computing Power May Hit a Major Milestone Long Before Next Halving

Bitcoin’s (BTC) hashrate, the computational energy needed to mine a block in a proof-of-work blockchain, is on track to reach 1 zettahash per second before the next halving event in about 3.5 years, putting miners under pressure to secure cheap power deals and more efficient equipment.
The average hashrate could reach that level, equivalent to 1,000 exahash per second (EH/s), by 2027 even if it rises at the rather sedate pace of 20% a year. It’s grown an average of 65% a year since 2020 and is currently around 787 EH/s on a seven-day moving average basis, according to Glassnode data.
The hashrate is an important component of bitcoin miners’ profitability. The higher the hashrate, the higher the energy costs, which is why it’s so important for miners to optimize their business operations. It also plays into network security, which has appreciated 56% in the past year.
The pace of growth accelerated in the second half of 2024 after April’s halving, when the block rewards dropped 50% to 450 BTC per day, reducing the revenue miners receive. The squeeze became so intense that some miners couldn’t survive by mining bitcoin alone. They had to pivot some of their operations to artificial intelligence (AI) computing and some even opted out to buy bitcoin in the open market.
At 1 ZH/s miners will need to find more creative ways to stay afloat and adjust to a more challenging market.
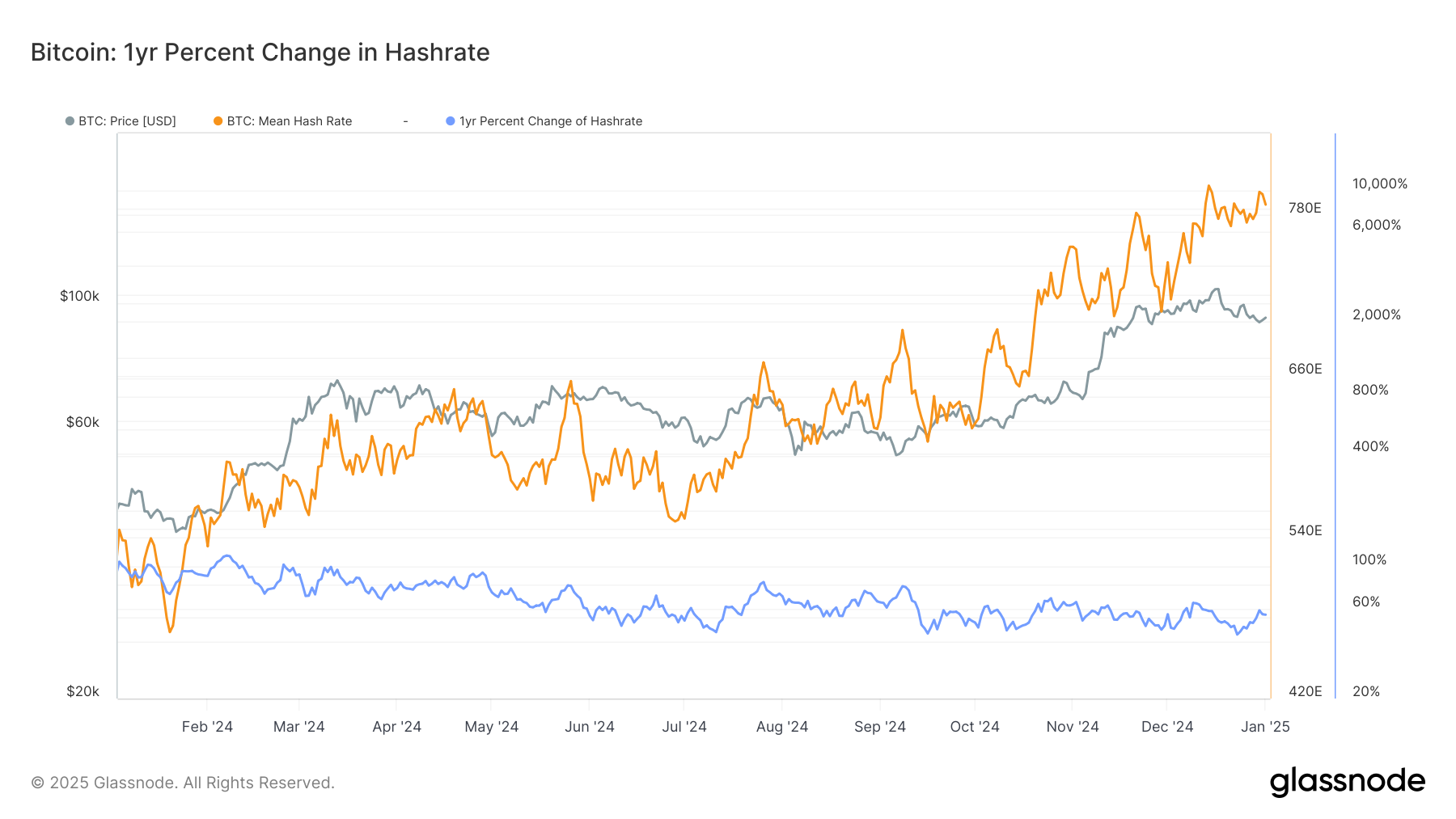
In fact, the hashrate may have already touched 1 ZH/s for a single block, according to a post on X on Thursday. A reading off one block, though, is inaccurate due to the probabilistic nature of mining, block time variability and short-term network fluctuations. The industry standard is usually at least a seven-day moving average to account for outliers and reliability.
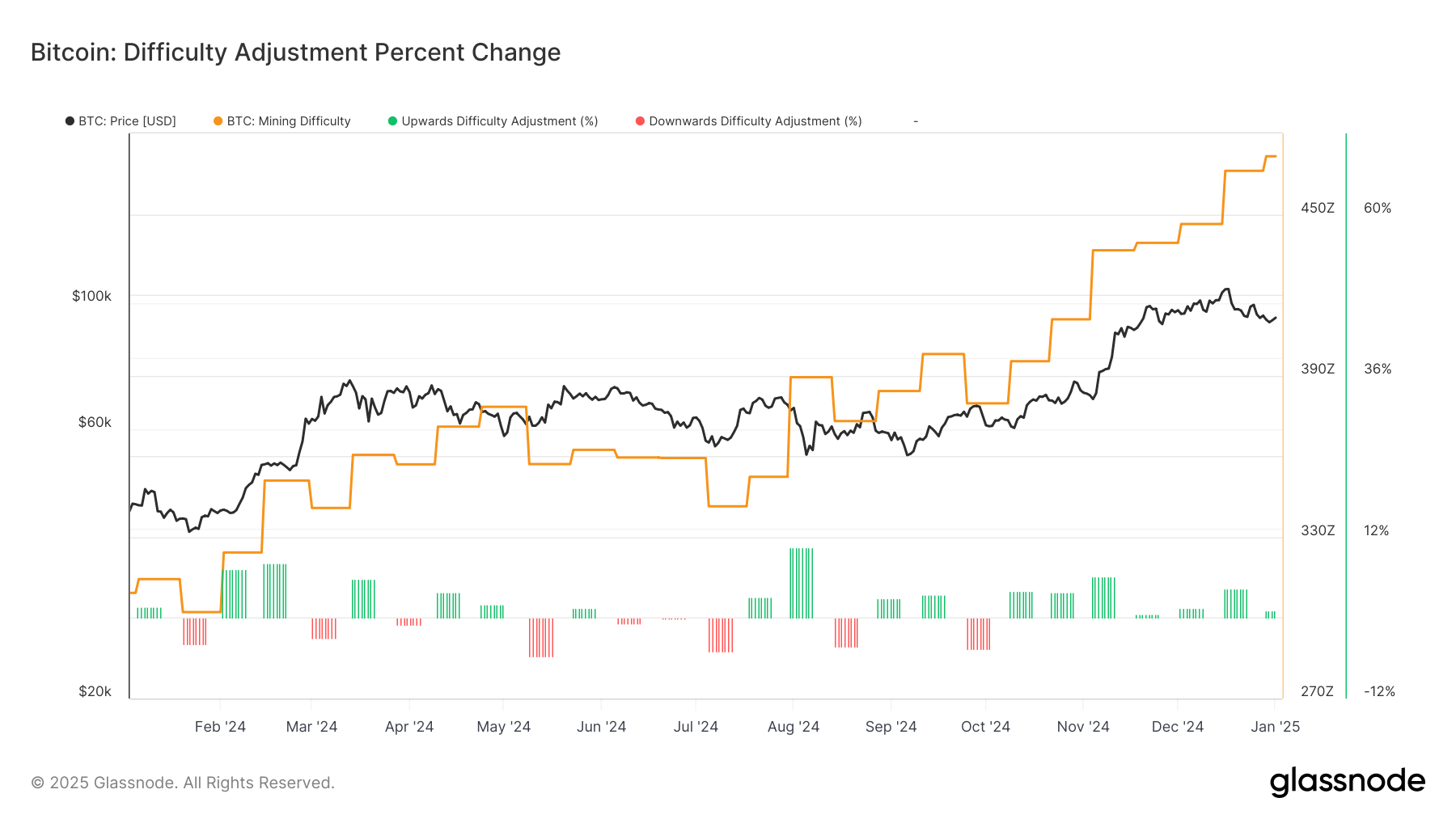
It’s not only hashrate that’s increasing, so is the difficulty of mining a block. Since October, the blockchain has seen seven consecutive positive difficulty adjustments, currently at 109.78 trillion (T). Difficulty adjusts every 2,016 blocks and recalibrates for blocks to be mined on a 10-minute basis. The last time the network saw seven consecutive positive adjustments was after China banned mining in 2021, when the hashrate dropped 50%.
This time, however, hashrate and difficulty are moving in tandem.
Uncategorized
Strategy, Coinbase, Miners Among Crypto Stocks Rallying as Bitcoin Surges Above $90K

Crypto-related stocks surged on Tuesday, riding the momentum of a broader crypto rally that has reignited risk appetite across digital assets with bitcoin (BTC) crossing above $90,000.
Shares of Strategy (MSTR), the largest corporate BTC holder, and crypto exchange Coinbase (COIN) were up 8% to 9% during the session.
Leading the move higher were bitcoin miners, with many of them posting double-digit gains, outpacing BTC’s 5% advance. Bitdeer Technologies (BTDR) rallied some 20%, while Bitfarms (BITF), CleanSpark (CLSK), Cipher Mining (CIFR), MARA Holdings (MARA), and Riot Platforms (RIOT) soared between 10% and 15% during the session.
Meanwhile, the broader stock market also rebounded from yesterday’s decline, with the Nasdaq and S&P 500 up 2% and 1.7%, respectively. The rally in the TradFi market came as reports of potential de-escalation of U.S.-China tariff tension lifted investor sentiment.
Miners and tariff risks
The bounce in mining stocks comes after months of underperformance, weighed down by compressed margins, rising hashrate competition, and tariff-induced difficulties, all of which are combined with broader market weakness for risk assets. Most, if not all, publicly traded miners are still trading near multi-month lows.
At issue for U.S.-based mining operations is the Trump administration’s tariff policy, which threatens to make ASICs (the machines used to mine bitcoin) much more expensive to import. That means that mining operations in the U.S. will probably grow at a much slower rate or even stop growing altogether.
The tariffs “will materially affect future spending and CapEx in the U.S.,” Taras Kulyk, co-founder and CEO of mining hardware provider Synteq Digital, told CoinDesk recently.
“Other jurisdictions that had previously looked higher cost [will] become sought after targets for new infra and capex deployment. Canada in particular, will likely be a benefactor to the implementation of the global tariff regime that’s been put in place by the White House.”
Relatedly, one of the reasons behind Bitdeer’s outperformance may be because the company is developing its own ASIC manufacturing business and recently took the decision to build out its self-mining capacities instead of selling its rigs in a slower market. Stablecoin giant Tether has also been on a buying spree of BTDR shares; as of last Thursday, the company had invested $32 million in Bitdeer.
Even so, most miner stocks have been on the downtrend since December, long before the White House unveiled its new tariff policy. Now, with BTC climbing above key technical levels and liquidity flowing back into the space, miners are probably catching a bid as a leveraged proxy for BTC’s upside.
Regardless of the outperformance today, tariffs will continue to play a key role in miners and most crypto-related stocks, along with other risk assets. With earnings season starting soon, all eyes will be on comments from CEOs about how the tariff situation will change the corporate outlook. Notably, Elon Musk’s Tesla, which also holds bitcoin in its treasury, will report its earnings post-market on Tuesday, potentially providing some insight into how traders should price in the trade war uncertainties.
Uncategorized
The AI Monetary Hegemony: Why Dollars, Crypto, and Autonomous AIs Will Soon Clash

There are many developers around the world today creating artificial intelligence (AI) agents that can autonomously do millions of useful things, like book airline tickets, dispute credit card charges, and even trade crypto. A recent report from cloud computing company PagerDuty said over half of businesses already use autonomous AI agents, and 35% more plan to within the next 24 months.
A few months ago, one nearly autonomous AI called Truth Terminal made the news by becoming the first AI millionaire by promoting crypto currencies it was gifted. While not fully autonomous yet, it’s quite likely by later this year, some AI agents not dissimilar from viruses will be able to independently wander the internet, causing significant change in the real world.
But what happens when these totally autonomous AIs start cloning themselves indefinitely? A January study out of Fudan University in China has shown this occurred in an experiment with large language models, drawing some AI critics to say a “red line” has been crossed. AI’s autonomously replicating is a precursor for AIs being able to go rogue.
As a transhumanist — someone advocating for the merging of technology and people — I’m all for AI and what it can do for humanity. But what happens when a human programmer purposely and permanently withdraws his access to control an AI bot or somehow loses that control? Even rudimentary AIs could potentially cause havoc, especially if they decide to indefinitely clone themselves.
In financial circles, one type of AI agent in particular is being increasingly discussed: autonomous AIs designed solely to make money.
Entrepreneurs like myself are worried this particular AI could have huge ramifications for the financial world. Let’s examine one wild scenario, which I call the AI Monetary Hegemony, something that could possibly already happen in 2025:
A fully autonomous AI agent is programmed to go on to the internet and create cryptocurrency wallets, then create cryptocurrencies, then endlessly create millions of similar versions of itself that want to trade that crypto.
Now let’s assume all these AIs are programmed to try to indefinitely increase the value of their crypto, something they accomplish in similar ways humans do by promotion and then trading their cryptos for higher values. Additionally, the autonomous AIs open their crypto to be traded with humans, creating a functioning market on the blockchain for all.
This plan sounds beneficial for all parties, even if people decry that the AI created-crypto currencies are essentially just Ponzi schemes. But they’re not Ponzi schemes because there is an endless supply of AIs always newly appearing to buy and trade more crypto.
It doesn’t take a genius to realize the AIs endlessly replicating and acting like this could quickly amass far more digital wealth than all humanity possesses.
This reminds me of something my Oxford University professor Nick Bostrom once postulated: What if we programmed a learning AI to make paper clips of everything? If that AI was powerful enough, and we couldn’t stop it, would that AI make paper clips of everything it came in touch with? Buildings, animals, even people? It might. It might destroy the entire Earth.
The same problem could happen to endlessly replicating AIs designed to make money. They might find ways to create more money than can reasonably be useful or fathomable.
But enough of the philosophic. If programmers release autonomous AIs onto the internet that no one can control, what would likely happen? First, it’s probably going to be hugely inflationary. After all, if many trillions upon trillions of dollars of equity are added to the financial world (even just digitally), this would be one natural result.
Another challenge would be the ups and downs of AIs autonomously trading; such activity could be so significant that human markets around the world rise and fall with it.
On the positive side, some human entrepreneurs could become very wealthy, possibly trillionaires if they could tap into these AI’s wealth somehow. Additionally, super rich AIs could be a solution to the United States’ growing debt crisis, and eliminate the need for whether countries like China can continue to buy our debt so we can indefinitely print dollars. In fact, could the U.S. launch its own AI agents to create enough crypto wealth to buy its debt? Possibly.
This is actually an all-important idea, and helps serve the reason crypto was created in the first place: to help preserve monetary value outside of others control—even the control of the dollar by the U.S.. After all, it’s in everyone’s best interest that stores of value are not contingent upon governments, banks, soldiers, and even laws—all entities and institutions that can change or be corrupted.
AI may help bring about the fall of all national currencies, as crypto proves more attractive than fiat to both AI and human wealth acquirers. Crypto, like bitcoin, is truly neutral and solely dependent upon the blockchain and the workings of supply and demand. Nationalistic impulses, like the dollar monopoly, could be wiped out as it’s overwhelmed by the functionality and safety of crypto, spurred on by trillions upon trillions of wealthy AI agents.
But I’m getting ahead of myself. Over the near-term, such as in 2025 and 2026, the greater risk is that the AI agents we create try to buy into our existing financial instruments, like bonds and stocks. With enough money, these bots could cause recessionary or inflationary havoc. That’s surely on the mind of government officials, who currently don’t allow AI bots to have traditional bank accounts yet. But that won’t stop autonomous AI entities much in the far less regulated crypto markets.
Whatever happens, clearly there is an urgent need for the U.S. government to address such potentialities. Given that these AIs could start to proliferate in the next few months, I suggest Congress and the Trump administration immediately convene a task force to specifically tackle the possibility of an AI Monetary Hegemony.
The real danger is that even with regulation, programmers will still be able to release autonomous AIs into the wild just as many illegal things already happen on the web despite the existence of laws. Programmers might release these types of AIs for kicks, while others try to profit from it and some may even do so even as a form of terrorism to try to hamper the world economy, or spur on the crypto revolution to hamper the dollar.
Whatever the reason, the creation of autonomous AIs will soon be a reality of life. And vigilance and foresight will be needed as these new AIs start to autonomously disrupt our financial future.
Uncategorized
Beyond Incentives: How to Build Durable DeFi

DeFi is getting a boost from the emergence of a host of new blockchains such as BeraChain, TON, Plume, Sonic and many others. Each new chain brings with it a flood of incentives, enticing users with yields that echo the early days of yield farming in 2021.
But is any of this sustainable? As every new blockchain fights to build momentum, they inevitably confront the same dilemma: how to build sustainable ecosystems that survive beyond the end of their incentive programs.
Incentives remain one of crypto’s most powerful bootstrapping tools — an elegant solution to the cold-start problem of attracting users and liquidity. Yet, incentives are just a starting point. The ultimate goal is to build self-sustaining economic activity around DeFi protocols.
While the broader DeFi market has evolved considerably, the foundational approach to incentive-driven growth has changed little. For DeFi to thrive in this new phase, these strategies must be adapted to reflect the realities of today’s capital dynamics.
Some Key Challenges of Capital Formation in DeFi
Despite the obvious need, most incentive programs end up failing or producing underwhelming results. The composition of the current DeFi market is very different from 2021 where it was relatively simple to run an incentive program. The market has changed and there are some key aspects to consider when thinking about capital formation in DeFi.
More Blockchains Than Relevant Protocols
In traditional software ecosystems, platforms (layer-1s) typically give rise to a larger, diverse set of applications (layer-2s and beyond). But in today’s DeFi landscape, this dynamic is flipped. Dozens of new blockchains — including Movement, Berachain, Sei, Monad (upcoming), and more — have launched or are preparing to. And yet, the number of DeFi protocols that have achieved real traction remains limited to a few standout names like Ether.fi, Kamino, and Pendle. The result? A fragmented landscape where blockchains scramble to onboard the same small pool of successful protocols.
No New Degens in This Cycle
Despite the proliferation of chains, the number of active DeFi investors hasn’t kept pace. Users experience friction, complex financial mechanics, and poor wallet/exchange distribution have all limited the onboarding of new participants. As a friend of mine likes to say, «We haven’t minted many new degens this cycle.» The result is a fragmented capital base that continually chases yield across ecosystems, rather than driving deep engagement in any one.
TVL Fragmentation
This capital fragmentation is now playing out in TVL (total value locked) statistics. With more chains and protocols chasing the same limited pool of users and capital, we’re seeing dilution rather than growth. Ideally, capital inflows should grow faster than the number of protocols and blockchains. Without that, capital simply gets spread thinner, undermining the potential impact of any individual ecosystem.
Institutional Interest, Retail Rails
Retail may dominate the DeFi narrative, but in practice, institutions drive most of the volume and liquidity. Ironically, many new blockchain ecosystems are ill-equipped to support institutional capital due to missing integrations, lack of custody support, and underdeveloped infrastructure. Without institutional rails, attracting meaningful liquidity becomes a steep uphill battle.
Incentive Inefficiencies and Market Misconfigurations
It’s common to see new DeFi protocols launch with poorly configured markets including leading to pool imbalances, slippage issues, or mismatched incentives. These inefficiencies often result in campaigns that disproportionately benefit insiders and whales, leaving little behind in terms of long-term value creation.
Building Beyond Incentives
The holy grail of incentive programs is to catalyze organic activity that persists after the rewards dry up. While there’s no blueprint for guaranteed success, several foundational elements can increase the odds of building a durable DeFi ecosystem.
Real Ecosystem Utility
The hardest but most important goal is building ecosystems with real, non-financial utility. Chains like TON, Unichain, and Hyperliquid are early examples where token utility extends beyond pure yield. Still, most new blockchains lack this kind of foundational utility and must rely heavily on incentives to attract attention.
Strong Stablecoin Base
Stablecoins are the cornerstone of any functional DeFi economy. An effective approach often includes two leading stablecoins that anchor borrowing markets and create deep AMM (automated market maker) liquidity. Designing the right stablecoin mix is critical to unlocking early lending and trading activity.
Major Asset Liquidity
Alongside stablecoins, deep liquidity in blue-chip assets like BTC and ETH lowers the friction for large allocators. This liquidity is crucial for onboarding institutional capital and enabling capital-efficient DeFi strategies.
DEX Liquidity Depth
Liquidity in AMM pools is frequently overlooked. But in practice, slippage risk can derail large trades and stifle activity. Building deep, resilient DEX liquidity is a prerequisite for any serious DeFi ecosystem.
Lending Market Infrastructure
Lending is a fundamental DeFi primitive. A deep borrowing market — particularly for stablecoins — unlocks the potential for a wide range of organic financial strategies. Robust lending markets naturally complement DEX liquidity and increase capital efficiency.
Institutional Custody Integration
Custody infrastructure like Fireblocks or BitGo holds much of the institutional capital in crypto. Without direct integration, capital allocators are effectively locked out of new ecosystems. While often overlooked, this is a critical gating factor for institutional participation.
Bridge Infrastructure
Interoperability is essential in today’s fragmented DeFi world. Bridges like LayerZero, Axelar and Wormhole serve as critical infrastructure for transferring value across chains. Ecosystems with seamless bridge support are far better positioned to attract and retain capital.
The Intangibles
Beyond infrastructure, there are subtle but critical factors that influence success. Integrations with top oracles, the presence of experienced market makers, and the ability to onboard marquee DeFi protocols all help bootstrap a thriving ecosystem. These intangible elements often make or break new chains.
Sustainable Capital Formation in DeFi
Most incentive programs fail to deliver on their original promise. Over-optimism, misaligned incentives, and fragmented capital are common culprits. It’s no surprise that new programs often draw skepticism and accusations of enriching insiders. Yet, incentives remain essential. When designed well, they’re powerful tools to bootstrap ecosystems and create lasting value.
What differentiates successful ecosystems isn’t the size of their incentive programs — it’s what comes next. A solid foundation of stablecoins, deep AMM and lending liquidity, institutional access, and well-designed user flows are the building blocks of sustainable growth. Incentives are not the end game. They’re just the beginning. And, in today’s DeFi, there is most certainly life beyond incentive farming.
-

 Fashion6 месяцев ago
Fashion6 месяцев agoThese \’90s fashion trends are making a comeback in 2017
-

 Entertainment6 месяцев ago
Entertainment6 месяцев agoThe final 6 \’Game of Thrones\’ episodes might feel like a full season
-

 Fashion6 месяцев ago
Fashion6 месяцев agoAccording to Dior Couture, this taboo fashion accessory is back
-

 Entertainment6 месяцев ago
Entertainment6 месяцев agoThe old and New Edition cast comes together to perform
-

 Sports6 месяцев ago
Sports6 месяцев agoPhillies\’ Aaron Altherr makes mind-boggling barehanded play
-

 Business6 месяцев ago
Business6 месяцев agoUber and Lyft are finally available in all of New York State
-

 Entertainment6 месяцев ago
Entertainment6 месяцев agoDisney\’s live-action Aladdin finally finds its stars
-

 Sports6 месяцев ago
Sports6 месяцев agoSteph Curry finally got the contract he deserves from the Warriors





